01.Part 1 · JavaScript 深度剖析
02.Part 2 · 前端工程化实战
02.模块二 模块化开发与规范化标准
05.任务五:webpack源码
01.内容概述

02.打包后文件分析




key: ‘src/inedx.js’, val(模块函数): (function(){})


03.单文件打包后源码调试














04.功能函数说明












05.CommonJS模块打包











06.eModule模块打包













07.功能函数手写实现
<!--index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="mybuilt.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
// mybuild.js
(function (modules) {
// 1. 用于缓存加载过的模块
let installedModules = {}
// 2. 定义一个 __webpack_require__ 方法来替换 import require 加载操作
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// 2-1 判断当前缓存中是否存在要被加载的模块内容,如果存在则直接返回
if (installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports
}
// 2-2 如果当前缓存中不存在则需要我们自己定义{} 执行被导入的模块内容加载
let module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId,
// 是否被加载
l: false,
// 导出内容
exports: {}
}
// 2-3 调用当前 moduleId 对应的函数,然后完成内容的加载
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__)
// 2-4 上述方法调用完成后,就可以修改 l 的值,表示当前模块已经加载完成
module.l = true
// 2-5 加载工作完成之后,要将拿回来的内容返回至调用的位置
return module.exports
}
// 3. 定义 m 属性用于保存 modules
__webpack_require__.m = modules
// 4. 定义 c 属性用于保存cache
__webpack_require__.c = installedModules
// 5. 定义 o 方法用于判断对象的身上是否存在指定的属性
__webpack_require__.o = function (object, property) {
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty(object, property)
}
// 6. 定义 d 方法用于在对象的身上添加指定的属性,同时给该属性提供gatter
__webpack_require__.d = function (exports, name, getter) {
// 对象身上没有该属性
if (!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {enumerable: true, get: getter})
}
}
// 7. 定义 r 方法用于标识当前模块是 es6(esModule) 类型
__webpack_require__.r = function (exports) {
if (typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, {value: "Module"})
}
Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', {value: true})
}
// 8. 定义 n 方法用于设置具体的getter
__webpack_require__.n = function (module) {
let getter = module && module.__esModule ?
function getDefault() {
return module['default']
} :
function getModuleExports() {
return module
}
// 给getter定义a属性,获取方法是getter
__webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter)
return getter
}
// 9. 定义 p 属性,用于保存资源访问路径
__webpack_require__.p = ""
// 10. 调用 __webpack_require__ 方法执行模块导入与加载操作
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = './src/index.js')
})
({
"./src/index.js":
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
var _login__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ./login */ "./src/login.js");
console.log('indexjs')
console.log(_login__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["default"], '<-----')
console.log(_login__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["age"], '<-----')
}),
"./src/login.js":
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
__webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "age", function () {
return age;
});
__webpack_exports__["default"] = ('我很帅');
const age = 18
})
})
// index.js
// let name = require('./login')
import name, {age} from './login'
console.log('indexjs')
console.log(name, '<-----')
console.log(age, '<-----')
// login.js
// module.exports = '拉勾教育'
export default '我很帅'
export const age = 18
09.懒加载实现流程梳理





在懒加载时生成script标签(e方法)来引入

10.t方法分析及实现




(function (modules) {
// ...
// 11. 定义 t 方法,用于加载指定 value 的模块内容,之后对内容进行处理再返回
__webpack_require__.t = function (value, mode) {
// 01 加载 value 对应的模块内容( value 一般就是模块id)
// 加载之后的内容又重新赋值给 value 变量
if (mode & 1) {
value = __webpack_require__(value)
}
if (mode & 8) { // 加载了可以直接返回使用的内容
return value
}
// 到这说明没有return
if ((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) {
return value
}
// 如果8和4都不成立,则需要自定义 ns 来通过 default 属性返回内容
let ns = Object.create(null)
__webpack_require__.r(ns)
Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', {enumerable: true, value: value})
if (mode & 2 && typeof value !== 'string') {
for (var key in value) {
__webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function (key) {
return value[key]
}.bin(null, key))
}
}
return ns
}
// 9. 定义 p 属性,用于保存资源访问路径
__webpack_require__.p = ""
// 10. 调用 __webpack_require__ 方法执行模块导入与加载操作
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = './src/index.js')
})
({
"./src/index.js":
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
// let name = __webpack_require__.t(/*! ./login */ "./src/login.js",0b1001)
let name = __webpack_require__.t(/*! ./login */ "./src/login.js", 0b0111)
console.log('index.js')
console.log(name)
}),
"./src/login.js":
(function (module, exports) {
module.exports = '拉勾教育'
})
})
11.单文件懒加载源码分析




























13.单文件懒加载手写实现



(function (modules) {
// 14. 定义 webpackJsonpCallback 实现: 合并模块定义,改变 promise 状态执行后续行为
function webpackJsonpCallback(data) {
// 1 获取需要被动态加载的模块 id
let chunkIds = data[0]
// 2 获取需要被动态加载的模块依赖关系对象
let moreModules = data[1]
let chunkId, resolves = []
// 3 循环判断 chunkIds 里对应的模块内容是否已经完成了加载
for (let i = 0; i < chunkIds.length; i++) {
chunkId = chunkIds[i]
if (
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(inStalledChunks, chunkId)
&& inStalledChunks[chunkId]
) {
resolves.push(inStalledChunks[chunkId][0])
}
// 更新当前 chunk 的状态
inStalledChunks[chunkId] = 0
}
for (moduleId in moreModules) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(moreModules, moduleId)) {
// 挂载动态加载的module的依赖关系到传入的modules
modules[moduleId] = moreModules[moduleId]
}
}
while (resolves.length) {
// 执行操作
resolves.shift()()
}
}
// 1. 用于缓存加载过的模块
let installedModules = {}
// 15 定义 inStalledChunks 对象,用于标识某个 chunkId 对应的 chunk 是否完成了加载
let inStalledChunks = {
// 0 -> 已加载
main: 0
}
// ...
// 17 定义 jsonpScriptSrc 来实现 src 的处理
function jsonpScriptSrc(chunkId) {
return __webpack_require__.p + "" + chunkId + ".built.js"
}
// 16 定义 e 方法用于实现: 实现jsonp来加载内容, 利用promise 实现异步加载操作
__webpack_require__.e = function (chunkId) {
// 1 定义一个数组用于存放 promise
let promises = []
// 2 获取 chunkId 对应的 chunk 是否已经完成了加载
let installedChunkData = inStalledChunks[chunkId]
// 3 依据当前是否已完成加载的状态来执行后续的逻辑
if (installedChunkData !== 0) {
if (installedChunkData) {
promises.push(installedChunkData[2])
} else {
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
installedChunkData = inStalledChunks[chunkId] = [resolve, reject]
})
// installedChunkData [resolve,reject,promise]
promises.push(installedChunkData[2] = promise)
// 创建标签
let script = document.createElement('script')
// 设置src
script.src = jsonpScriptSrc(chunkId)
// 写入 script 标签
document.head.appendChild(script)
}
}
// 执行promise
return Promise.all(promises)
}
// ...
// 11/2. 定义变量存放数组
let jsonArray = window['webpackJsonp'] = window['webpackJsonp'] || []
// 12. 保存原生的push方法
let oldJsonpFunction = jsonArray.push.bind(jsonArray)
// 13. 重写push方法
jsonArray.push = webpackJsonpCallback
// ...
})
({
"./src/index.js":
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
let oBtn = document.getElementById('btn')
oBtn.addEventListener('click', function () {
__webpack_require__.e(/*! import() | login */ "login").then(__webpack_require__.t.bind(null, /*! ./login */ "./src/login.js", 7)).then((login) => {
console.log(login)
})
})
console.log('index.js')
})
});
14.webpack 与 tapable












15.同步钩子使用及调试


const {SyncHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new SyncHook(['name', 'age'])
// 定义
hook.tap('fn1', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn1--->', name, age)
})
hook.tap('fn2', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
})
// 调用
hook.call('zoe', 18)
const {SyncBailHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new SyncBailHook(['name', 'age'])
// 定义
hook.tap('fn1', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn1--->', name, age)
})
// 返回undefined不会熔断
hook.tap('fn2', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
return undefined
})
// 返回!undefined会熔断
hook.tap('fn2', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
return 'ret2'
})
hook.tap('fn3', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn3--->', name, age)
})
// 调用
hook.call('lg', 100)
const {SyncWaterfallHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new SyncWaterfallHook(['name', 'age'])
// 定义
hook.tap('fn1', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn1--->', name, age)
return 'ret1'
})
// 返回undefined不会熔断
hook.tap('fn2', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
return 'ret2'
})
// 返回!undefined会熔断
hook.tap('fn3', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn3--->', name, age)
return 'ret3'
})
hook.call('water', 3)
const {SyncLoopHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new SyncLoopHook(['name', 'age'])
let count1 = 0
let count2 = 0
let count3 = 0
// 定义
hook.tap('fn1', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn1--->', name, age)
if (++count1 === 1) {
count1 = 0
// 返回undefined退出loop
return undefined
}
return true
})
// 返回undefined不会熔断
hook.tap('fn2', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
// 不满足条件,从头开始(fn1)执行
// count++ -> count+=1
if (++count2 === 2) {
count2 = 0
return undefined
}
return true
})
// 返回!undefined会熔断
hook.tap('fn3', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn3--->', name, age)
if (++count3 === 3) {
count3 = 0
return undefined
}
return true
})
hook.call('foo', 33)
16.异步钩子使用
const {AsyncParallelHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new AsyncParallelHook(['name'])
// 异步钩子的使用,有三种方式: tap tapAsync tapPromise
// hook.tap('fn1', function (name) {
// console.log('fn1--->', name)
// })
//
// hook.tap('fn2', function (name) {
// console.log('fn2--->', name)
// })
//
// hook.callAsync('zoe', function () {
// console.log('last callback')
// })
// console.time('time')
// hook.tapAsync('fn1', function (name, callback) {
// setTimeout(() => {
// console.log('fn1--->', name)
// callback()
// }, 1000)
// })
//
// hook.tapAsync('fn2', function (name, callback) {
// setTimeout(() => {
// console.log('fn2--->', name)
// callback()
// }, 2000)
// })
//
// hook.callAsync('lg', function () {
// console.log('last callback')
// console.timeEnd('time')
// })
console.time('time')
hook.tapPromise('fn1', function (name) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn1--->', name)
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
})
hook.tapPromise('fn2', function (name) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn2--->', name)
resolve()
}, 2000)
})
})
hook.promise('foo').then(() => {
console.log('end')
console.timeEnd('time')
})
const {AsyncParallelBailHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new AsyncParallelBailHook(['name'])
console.time('time')
hook.tapAsync('fn1', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn1--->', name)
callback()
}, 1000)
})
hook.tapAsync('fn2', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn2--->', name)
// 参数1是错误
callback('err')
}, 2000)
})
hook.tapAsync('fn3', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn3--->', name)
callback()
}, 3000)
})
hook.callAsync('zce', function () {
console.log('last callback')
console.timeEnd('time')
})
const {AsyncSeriesHook} = require('tapable')
let hook = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name'])
console.time('time')
hook.tapPromise('fn1', function (name) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn1--->', name)
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
})
hook.tapPromise('fn2', function (name) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('fn2--->', name)
resolve()
}, 2000)
})
})
hook.promise('zce').then(() => {
console.log('last callback')
console.timeEnd('time') // 3
})
17.SyncHook源码调试



























19.手写 SyncHook

// useHook.js
// const {SyncHook} = require('tapable')
const SyncHook = require("./SyncHook");
let hook = new SyncHook(['name', 'age'])
hook.tap('fn1', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn1--->', name, age)
})
hook.tap('fn2', function (name, age) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
})
hook.call('zoeee', 18)
// SyncHook.js
const Hook = require('./Hook')
class HookCodeFactory {
args() {
// ['name','age'] --(to str)--> name,age
return this.options.args.join(',')
}
head() {
return `var _x = this._x;`
}
content() {
let code = ``
for (let i = 0; i < this.options.taps.length; i++) {
code += `var _fn${i} = _x[${i}];_fn${i}(${this.args()});`
}
return code
}
// instance是hook实例
// options是{tags:[{},{}],args:[name,age]}
setup(instance, options) { // 准备后续要用到的数据
// tapable源码中,这里通过init方法实现
// 我们这里直接挂载到this上
this.options = options
// this._x = [f1,f2,...]
instance._x = options.taps.map(o => o.fn)
}
create() { // 核心是创建可执行的代码体,然后返回
let fn
// fn=new Function ("name, age","var _x = this._x, var _fn0 = x[0]; _fn0(name, age);")
fn = new Function(
this.args(),
this.head() + this.content()
)
return fn
}
}
let factory = new HookCodeFactory()
class SyncHook extends Hook {
constructor(args) {
super(args)
}
compile(options) {
factory.setup(this, options)
return factory.create(options)
}
}
module.exports = SyncHook
// Hook.js
class Hook {
constructor(args = []) {
this.args = args
this.taps = [] // 用于存放组装好的 {}
this._x = undefined // 将来在代码工厂函数中会给 _x = [f1,f2,...]
}
tap(options, fn) {
if (typeof options === 'string') {
options = {name: options}
}
// 合并 {fn: ..., name: fn1}
options = Object.assign({fn}, options)
// 将组装好的options添加到[]
this._insert(options)
}
_insert(options) {
this.taps[this.taps.length] = options
}
call(...args) {
// 1. 创建将来要具体执行的函数代码结构
let callFn = this._createCall()
// 2. 调用函数
return callFn.apply(this, args)
}
_createCall() {
return this.compile({
taps: this.taps,
args: this.args
})
}
}
module.exports = Hook
21.AyncParallelHook源码分析















// useHook.js
const AsyncParallelHook = require('./AsyncParallelHook')
let hook = new AsyncParallelHook(['name', 'age'])
hook.tapAsync('fn1', function (name, age, callback) {
console.log('fn1--->', name, age)
callback()
})
hook.tapAsync('fn2', function (name, age, callback) {
console.log('fn2--->', name, age)
callback()
})
hook.callAsync('zoeee', 18, function () {
console.log('end~')
})
// hook.js
class Hook {
// ...
tapAsync(options, fn) {
if (typeof options === 'string') {
options = {name: options}
}
options = Object.assign({fn}, options) // {fn:..., name:fn1}
// 调用方法将组装好的options添加到[]
this._insert(options)
}
callAsync(...args) {
let callFn = this._createCall()
return callFn.apply(this, args)
}
}
module.exports = Hook
// AsyncParallelHook.js
const Hook = require('./Hook')
class HookCodeFactory {
args({after, before} = {}) {
let allArgs = this.options.args
// before拼接allArgs
if (before) allArgs = [before].concat(allArgs)
// allArgs拼接after
if (after) allArgs = allArgs.concat(after)
// ['name','age'] --(to str)--> name,age
return allArgs.join(',')
}
head() {
return `"use strict";var _context;var _x = this._x;`
}
content() {
let code = `
var _counter = ${this.options.taps.length};
var _done = (function (){ _callback(); });
`
for (let i = 0; i < this.options.taps.length; i++) {
code += `var _fn${i} = _x[${i}];_fn${i}(name, age, (function (){
if (--_counter === 0) _done();
}));
`
}
return code
}
// instance是hook实例
// options是{tags:[{},{}],args:[name,age]}
setup(instance, options) { // 准备后续要用到的数据
// tapable源码中,这里通过init方法实现
// 我们这里直接挂载到this上
this.options = options
// this._x = [f1,f2,...]
instance._x = options.taps.map(o => o.fn)
}
create() { // 核心是创建可执行的代码体,然后返回
let fn
// fn=new Function ("name, age","var _x = this._x, var _fn0 = x[0]; _fn0(name, age);")
fn = new Function(
this.args({after: '_callback'}),
this.head() + this.content()
)
return fn
}
}
let factory = new HookCodeFactory()
class AsyncParallelHook extends Hook {
constructor(args) {
super(args)
}
compile(options) {
factory.setup(this, options)
return factory.create(options)
}
}
module.exports = AsyncParallelHook
23.定位 webpack 打包入口

















24.编译主流程调试

















25.手写 webpack.js 实现

// run.js
let webpack = require('./lgPack')
let options = require('./webpack.config')
let compiler = webpack(options)
compiler.run((err, stats) => {
console.log(err)
console.log(stats.toJson({
entries: true,
chunks: false,
modules: false,
assets: false
}))
})
// webpack.config.js
let webpack = require('./lgPack')
let options = require('./webpack.config')
let compiler = webpack(options)
compiler.run((err, stats) => {
console.log(err)
console.log(stats.toJson({
entries: true,
chunks: false,
modules: false,
assets: false
}))
})

// lgPack/lib/webpack.js
const Compiler = require('./Compiler')
const NodeEnvironmentPlugin = require('./node/NodeEnvironmentPlugin')
const webpack = function (options) {
// 1. 实例化compiler对象
let compiler = new Compiler(options.context)
compiler.options = options
// 2. 初始化NodeEnvironmentPlugin(让compiler具备文件读写能力)
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin().apply(compiler)
// 3. 挂载所有的plugins插件至compiler对象身上
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
plugin.apply(compiler)
}
}
// 4. 挂载所有webpack内置的插件(入口)
// compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler)
// 5. 返回compiler对象
return compiler
}
module.exports = webpack
// lgPack/lib/Compiler.js
const {
Tapable, AsyncSeriesHook
} = require('tapable')
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.context = context
this.hooks = {
done: new AsyncSeriesHook(['stats']),
}
}
run(callback) {
callback(null, {
toJson() {
return {
entries: [], // 当前次打包的入口信息
chunks: [], // 当前次打包的chunk信息
modules: [], // 模块信息
assets: [], // 当前次打包最终生成的资源
}
}
})
}
}
module.exports = Compiler
// lgPack/lib/node/NodeEnvironmentPlugin.js
const fs = require("fs");
class NodeEnvironmentPlugin {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options || {}
}
apply(compiler) {
// compiler可以调用fs,得到文件读写能力
compiler.inputFileSystem = fs
compiler.outputFileSystem = fs
}
}
module.exports = NodeEnvironmentPlugin
26.EntryOptionPlugin 分析










27.EntryOptionPlugin流程手写
// webpack.js
const Compiler = require('./Compiler')
const NodeEnvironmentPlugin = require('./node/NodeEnvironmentPlugin')
const WebpackOptionsApply = require('./WebpackOptionsApply')
const webpack = function (options) {
// ...
// 4. 挂载所有webpack内置的插件(入口)
compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler)
// 5. 返回compiler对象
return compiler
}
module.exports = webpack
// WebpackOptionsApply.js
const EntryOptionPlugin = require("./EntryOptionPlugin");
class WebpackOptionsApply {
process(options, compiler) {
new EntryOptionPlugin().apply(compiler)
compiler.hooks.entryOption.call(options.context, options.entry)
}
}
module.exports = WebpackOptionsApply
// EntryOptionPlugin.js
const SingleEntryPlugin = require("./SingleEntryPlugin");
function itemToPlugin(context, item, name) {
return new SingleEntryPlugin(context, item, name)
}
class EntryOptionPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.entryOption.tap('EntryOptionPlugin', (context, entry) => {
itemToPlugin(context, entry, "main").apply(compiler)
})
}
}
module.exports = EntryOptionPlugin
// SingleEntryPlugin.js
class SingleEntryPlugin {
constructor(context, entry, name) {
this.context = context
this.entry = entry
this.name = name
}
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.make.tapAsync('SingleEntryPlugin', (compilation, callback) => {
const {context, entry, name} = this
console.log("make 方法执行")
// compilation.addEntry(context, entry, name, callback)
})
}
}
module.exports = SingleEntryPlugin
// Compiler.js
const {
Tapable, AsyncSeriesHook, SyncBailHook, SyncHook, AsyncParallelHook
} = require('tapable')
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.context = context
this.hooks = {
done: new AsyncSeriesHook(['stats']),
entryOption: new SyncBailHook(['context', 'entry']),
beforeCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["params"]),
compile: new SyncHook(["params"]),
make: new AsyncParallelHook(["compilation"]),
afterCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
}
}
run(callback) {
// ...
}
}
module.exports = Compiler
28.run方法分析及实现



// Compiler.js
const {
Tapable, AsyncSeriesHook, SyncBailHook, SyncHook, AsyncParallelHook
} = require('tapable')
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.context = context
this.hooks = {
done: new AsyncSeriesHook(['stats']),
entryOption: new SyncBailHook(['context', 'entry']),
beforeCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["params"]),
compile: new SyncHook(["params"]),
make: new AsyncParallelHook(["compilation"]),
afterCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
thisCompilation: new SyncHook(["compilation", "params"]),
compilation: new SyncHook(["compilation", "params"]),
beforeRun: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"]),
run: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"]),
}
}
run(callback) {
console.log('run 方法执行')
const finalCallback = function (err, stats) {
callback(err, stats)
}
const onCompiled = function (err, compilation) {
console.log('onCompiled')
finalCallback(err, {
toJson() {
return {
entries: [],
chunk: [],
modules: [],
assets: []
}
}
})
}
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(this, (err) => {
this.hooks.run.callAsync(this, (err) => {
this.compile(onCompiled)
})
})
}
compile(callback) {
}
}
module.exports = Compiler
29.compile 分析及实现






// Compiler.js
const {
Tapable, AsyncSeriesHook, SyncBailHook, SyncHook, AsyncParallelHook
} = require('tapable')
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const Compilation = require("./Compilation");
class Compiler extends Tapable {
// ...
compile(callback) {
const params = this.newCompilationParams()
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(params, (err) => {
this.hooks.compile.call(params)
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params)
this.hooks.make.callAsync(compilation, (err) => {
console.log('make钩子监听触发')
callback()
})
})
}
newCompilationParams() {
const params = {
// normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
normalModuleFactory: new NormalModuleFactory()
}
return params;
}
newCompilation(params) {
return this.createCompilation()
}
createCompilation() {
// Compilation 代表某一次编译, Compiler 代表整个编译流程
return new Compilation(this)
}
}
module.exports = Compiler
30.make 前流程回顾
















31.addEntry 流程分析



































33.addEntry 初始化
// compilation.js
const {Tapable} = require("tapable")
class Compilation extends Tapable {
constructor(compiler) {
super()
this.compiler = compiler
this.context = compiler.context
this.options = compiler.options
// compilation具备文件读写能力
this.inputFileSystem = compiler.inputFileSystem
this.outputFileSystem = compiler.outputFileSystem
this.entries = [] // 存放所有入口模块
this.modules = [] // 存放所有模块
this.hooks = {
succeedModule: new SyncHook(['module'])
}
}
/**
* 完成模块编译
* @param context 当前项目的根
* @param entry 当前入口的相对路径
* @param name chunkName: main
* @param callback 回调
*/
addEntry(context, entry, name, callback) {
this._addModuleChain(context, entry, name, (err, module) => {
callback(err, module)
})
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
34._addModuleChain实现
// Compilation.js
const {Tapable} = require("tapable")
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
class Compilation extends Tapable {
// ...
_addModuleChain(context, entry, name, callback) {
let entryModule = normalModuleFactory.create({
name, context,
rawRequest: entry,
// 相对路径拼接成当前目录的绝对路径
resource: path.posix.join(context, entry),
// todo: parser
})
const afterBuild = function (err) {
callback(err, entryModule)
}
this.buildModule(entryModule, afterBuild)
// 完成本次build后, 保存模块
this.entries.push(entryModule)
this.modules.push(entryModule)
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
// NormalModuleFactory.js
const NormalModule = require("./NormalModule");
class NormalModuleFactory {
create(data) {
return new NormalModule(data)
}
}
module.exports = NormalModuleFactory
// NormalModule.js
class NormalModule {
constructor(data) {
this.name = data.name
this.entry = data.entry
this.rawRequest = data.rawRequest
this.parser = data.parser
// todo: 等待完成
this.resource = data.resource
this._source // 存放某个模块的源代码
this._ast // 存放某个模块源代码的 ast
}
}
module.exports = NormalModule
35.buildModule实现

// Compilation.js
const {Tapable} = require("tapable")
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
const parser = new Parser()
class Compilation extends Tapable {
// ...
/**
* 完成具体的 build 行为
* @param module 当前需要被编译的模块
* @param callback
*/
buildModule(module, callback) {
// module -> entryModule
module.build(this, (err) => {
// 走到这里表示当前代码编译完成
this.hooks.succeedModule.call(module)
callback(err, module)
})
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
// NormalModule.js
class NormalModule {
constructor(data) {
this.name = data.name
this.entry = data.entry
this.rawRequest = data.rawRequest
this.parser = data.parser
// todo: 等待完成
this.resource = data.resource
this._source // 存放某个模块的源代码
this._ast // 存放某个模块源代码的 ast
}
build(compilation, callback) {
this.doBuild(compilation, (err) => {
this._ast = this.parser.parse(this._source)
callback(err)
})
}
doBuild(component, callback) {
this.getSource(compilation, (err, source) => {
this._source = source
callback()
})
}
getSource(compilation, callback) {
compilation.inputFileSystem.readFile(this.resource, 'utf-8', callback)
}
}
module.exports = NormalModule
36.build及parser 实现
npm i babylon -D
// Parser.js
const babylon = require('babylon')
const {Tapable} = require("tapable");
class Parser extends Tapable {
parse(source) {
return babylon.parse(source, {
sourceType: 'module',
// 当前插件支持动态导入的语法
plugins: ['dynamicImport'],
})
}
}
module.exports = Parser
// Stats.js
class Stats {
constructor(compilation) {
this.entries = compilation.entries
this.modules = compilation.modules
}
toJson() {
return this
}
}
module.exports = Stats


37.依赖模块处理









// NormalModule.js
const path = require("path");
// 提供修改ast节点的方法
const types = require('@babel/types')
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default
const traverse = require("@babel/traverse").default
class NormalModule {
constructor(data) {
// process.cwd()
this.context = data.context
this.name = data.name
// this.entry = data.entry
this.rawRequest = data.rawRequest
this.parser = data.parser
// todo: 等待完成
this.resource = data.resource // 文件绝对路径
this._source // 存放某个模块的源代码
this._ast // 存放某个模块源代码的 ast
this.dependencies = [] // 定义一个空数组保存被依赖加载的模块信息
}
build(compilation, callback) {
this.doBuild(compilation, (err) => {
this._ast = this.parser.parse(this._source)
// 修改ast
traverse(this._ast, {
CallExpression: (nodePath) => {
// 拿到ast上的node
let node = nodePath.node
// 定位require所在节点
if (node.callee.name === 'require') {
// 获取原始请求路径
let modulePath = node.arguments[0].value // './title'
// 取出当前被加载的模块名称(根据分隔符拆分)
// path.posix.sep -> 拿到当前操作系统的分隔符
let moduleName = modulePath.split(path.posix.sep).pop() // title
// 当前我们只能打包处理js
// moduleName有 . 表示有指定后缀, 没有就默认指定为js
let extName = moduleName.indexOf('.') === -1 ? '.js' : ''
moduleName += extName // title.js
// 最终要有绝对路径, 以便读取文件
// 拼接当前文件的父目录 和 导入文件名
let depResource = path.posix.join(path.posix.dirname(this.resource), moduleName)
// 定义当前模块的id
// this.context - depResource -> ./src/title.js
let depModuleId = './' + path.posix.relative(this.context, depResource)
// 记录当前被依赖模块的信息, 方便后面加载
this.dependencies.push({
name: this.name, // todo 动态修改
context: this.context,
rawRequest: moduleName,
moduleId: depModuleId,
resource: depResource
})
// 替换内容
node.callee.name = '__webpack_require__'
// types.stringLiteral 创建string类型的值
// node.arguments 替换为 depModuleId (string)
node.arguments = [types.stringLiteral(depModuleId)]
}
}
})
// 将修改后的ast转为code(可执行代码)
let {code} = generator(this._ast)
this._source = code
callback(err)
})
}
// ...
}
module.exports = NormalModule
// Compilation.js
const {Tapable, SyncHook} = require("tapable")
const Parser = require('./Parser')
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
const parser = new Parser()
class Compilation extends Tapable {
// ...
_addModuleChain(context, entry, name, callback) {
let entryModule = normalModuleFactory.create({
name, context,
rawRequest: entry,
// 相对路径拼接成当前目录的绝对路径
resource: path.posix.join(context, entry),
parser
})
const afterBuild = function (err, module) {
// 需要判断当前module加载完成之后是否需要处理依赖加载
if (module.dependencies.length > 0) {
// 当前逻辑表示module有需要依赖加载的模块, 单独定义一个方法实现
this.processDependencies(module, (err) => {
callback(err, module)
})
} else {
callback(err, module)
}
}
this.buildModule(entryModule, afterBuild)
// 完成本次build后, 保存模块
this.entries.push(entryModule)
this.modules.push(entryModule)
}
// ...
processDependencies(module, callback) {
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
39.抽离createModule方法
// Compilation.js
const {Tapable, SyncHook} = require("tapable")
const Parser = require('./Parser')
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
const parser = new Parser()
class Compilation extends Tapable {
// ...
_addModuleChain(context, entry, name, callback) {
this.createModule({
parser,
name: name,
context: context,
// 原始请求路径
rawRequest: entry,
resource: path.posix.join(context, entry),
moduleId: './' + path.posix.relative(context, path.posix.join(context, entry))
}, (entryModule) => {
this.entries.push(entryModule)
}, callback)
}
/**
* 创建模块的方法
* @param data 创建模块需要的属性值
* @param doAndEntry 可选参数, 在加载入口模块的时候, 将入口模块的id 写入 this.entries
* @param callback
*/
createModule(data, doAndEntry, callback) {
let module = normalModuleFactory.create(data)
const afterBuild = (err, module) => {
// 需要判断当前module加载完成之后是否需要处理依赖加载
if (module.dependencies.length > 0) {
// 当前逻辑表示module有需要依赖加载的模块, 单独定义一个方法实现
this.processDependencies(module, (err) => {
callback(err, module)
})
} else {
callback(err, module)
}
}
this.buildModule(module, afterBuild)
// 完成本次build后, 保存模块
// this.entries.push(module)
this.modules.push(module)
doAndEntry && doAndEntry(module)
}
// ...
}
module.exports = Compilation
40.编译依赖模块
// Compilation.js
const {Tapable, SyncHook} = require("tapable")
const Parser = require('./Parser')
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const async = require('neo-async')
const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
const parser = new Parser()
class Compilation extends Tapable {
// ...
processDependencies(module, callback) {
// 实现被依赖模块的加载
// 创建对应模块,然后想办法拿出其中的内容
// 在所有被依赖模块加载完后再 callback
let dependencies = module.dependencies
async.forEach(dependencies, (dependency, done) => {
// 调用done表示执行完毕
this.createModule({
parser,
name: dependency.name,
context: dependency.context,
rawRequest: dependency.rawRequest,
moduleId: dependency.moduleId,
resource: dependency.resource
}, null, done)
}, callback)
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
41.chunk流程分析及实现
// Compilation.js
const {Tapable, SyncHook} = require("tapable")
const Parser = require('./Parser')
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const async = require('neo-async')
const Chunk = require("./Chunk");
const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
const parser = new Parser()
class Compilation extends Tapable {
constructor(compiler) {
super()
this.compiler = compiler
this.context = compiler.context
this.options = compiler.options
// compilation具备文件读写能力
this.inputFileSystem = compiler.inputFileSystem
this.outputFileSystem = compiler.outputFileSystem
this.entries = [] // 存放所有入口模块
this.modules = [] // 存放所有模块
this.chunks = [] // 存放当前次打包产出的chunk
this.hooks = {
succeedModule: new SyncHook(['module']),
seal: new SyncHook(),
beforeChunks: new SyncHook(),
afterChunks: new SyncHook(),
}
}
// ...
// 封装chunk
seal(callback) {
this.hooks.seal.call()
this.hooks.beforeChunks.call()
// 所有入口模块都存放在了 compilation 对象的 entires 数组里
// 封装 chunk 就是根据某个入口,将它所有依赖和源代码放在一起,之后做合并
for (const entryModule of this.entries) {
// 核心:创建模块加载已有模块内容,同时记录模块信息
const chunk = new Chunk(entryModule)
this.chunks.push(chunk)
// 给chunk赋值
chunk.modules = this.modules.filter(module => module.name === chunk.name)
}
callback()
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
// Compiler.js
const {
Tapable, AsyncSeriesHook, SyncBailHook, SyncHook, AsyncParallelHook
} = require('tapable')
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const Compilation = require("./Compilation");
const Stats = require("./Stats");
class Compiler extends Tapable {
//...
compile(callback) {
const params = this.newCompilationParams()
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(params, (err) => {
this.hooks.compile.call(params)
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params)
this.hooks.make.callAsync(compilation, (err) => {
// console.log('make钩子监听触发')
// callback(err,compilation)
// 处理chunk
compilation.seal((err) => {
this.hooks.afterCompile.callAsync(compilation, (err) => {
callback(err, compilation)
})
})
})
})
}
// ...
}
module.exports = Compiler
// Stats.js
class Stats {
constructor(compilation) {
this.entries = compilation.entries
this.modules = compilation.modules
this.chunks = compilation.chunks
}
toJson() {
return this
}
}
module.exports = Stats
// Chunk.js
class Chunk {
constructor(entryModule) {
this.entryModule = entryModule
this.name = entryModule.name
this.files = [] // 打包后文件名称
this.modules = [] // 当前chunk里的所有模块
}
}
module.exports = Chunk
42.生成chunk代码
// Compilation.js
const {Tapable, SyncHook} = require("tapable")
const Parser = require('./Parser')
const path = require("path");
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const async = require('neo-async')
const Chunk = require("./Chunk");
const ejs = require('ejs')
const normalModuleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory()
const parser = new Parser()
class Compilation extends Tapable {
constructor(compiler) {
super()
this.compiler = compiler
this.context = compiler.context
this.options = compiler.options
// compilation具备文件读写能力
this.inputFileSystem = compiler.inputFileSystem
this.outputFileSystem = compiler.outputFileSystem
this.entries = [] // 存放所有入口模块
this.modules = [] // 存放所有模块
this.chunks = [] // 存放当前次打包产出的chunk
this.assets = []
this.files = []
this.hooks = {
succeedModule: new SyncHook(['module']),
seal: new SyncHook(),
beforeChunks: new SyncHook(),
afterChunks: new SyncHook(),
}
}
// ...
// 封装chunk
seal(callback) {
this.hooks.seal.call()
this.hooks.beforeChunks.call()
// 所有入口模块都存放在了 compilation 对象的 entires 数组里
// 封装 chunk 就是根据某个入口,将它所有依赖和源代码放在一起,之后做合并
for (const entryModule of this.entries) {
// 核心:创建模块加载已有模块内容,同时记录模块信息
const chunk = new Chunk(entryModule)
this.chunks.push(chunk)
// 给chunk赋值
chunk.modules = this.modules.filter(module => module.name === chunk.name)
}
// chunk流程处理完就进入chunk代码处理环节(模板文件+模块中的源代码 -> chunk.js)
this.hooks.afterChunks.call(this.chunks)
// 生成代码内容
this.createChunkAssets()
callback()
}
createChunkAssets() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.chunks.length; i++) {
const chunk = this.chunks[i]
const fileName = chunk.name + '.js'
chunk.files.push(fileName)
// 生成具体的chunk内容
// 获取模板文件的路径
let tempPath = path.posix.join(__dirname, 'temp/main.ejs')
// 读取模块文件中的内容
let tempCode = this.inputFileSystem.readFileSync(tempPath, 'utf-8')
// 获取渲染函数
let tempRender = ejs.compile(tempCode)
// 渲染数据
let source = tempRender({
entryModuleId: chunk.entryModule.moduleId,
modules: chunk.modules
})
// 输出文件
this.emitAssets(fileName, source)
}
}
emitAssets(fileName, source) {
this.assets[fileName] = source
this.files.push(fileName)
}
}
module.exports = Compilation
// lib/temp/main.ejs
(function (modules) {
// 14. 定义 webpackJsonpCallback 实现: 合并模块定义,改变 promise 状态执行后续行为
function webpackJsonpCallback(data) {
// 1 获取需要被动态加载的模块 id
let chunkIds = data[0]
// 2 获取需要被动态加载的模块依赖关系对象
let moreModules = data[1]
let chunkId, resolves = []
// 3 循环判断 chunkIds 里对应的模块内容是否已经完成了加载
for (let i = 0; i < chunkIds.length; i++) {
chunkId = chunkIds[i]
if (
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(inStalledChunks, chunkId)
&& inStalledChunks[chunkId]
) {
resolves.push(inStalledChunks[chunkId][0])
}
// 更新当前 chunk 的状态
inStalledChunks[chunkId] = 0
}
for (moduleId in moreModules) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(moreModules, moduleId)) {
// 挂载动态加载的module的依赖关系到传入的modules
modules[moduleId] = moreModules[moduleId]
}
}
while (resolves.length) {
// 执行操作
resolves.shift()()
}
}
// 1. 用于缓存加载过的模块
let installedModules = {}
// 15 定义 inStalledChunks 对象,用于标识某个 chunkId 对应的 chunk 是否完成了加载
let inStalledChunks = {
// 0 -> 已加载
main: 0
}
// 2. 定义一个 __webpack_require__ 方法来替换 import require 加载操作
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// 2-1 判断当前缓存中是否存在要被加载的模块内容,如果存在则直接返回
if (installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports
}
// 2-2 如果当前缓存中不存在则需要我们自己定义{} 执行被导入的模块内容加载
let module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId,
// 是否被加载
l: false,
// 导出内容
exports: {}
}
// 2-3 调用当前 moduleId 对应的函数,然后完成内容的加载
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__)
// 2-4 上述方法调用完成后,就可以修改 l 的值,表示当前模块已经加载完成
module.l = true
// 2-5 加载工作完成之后,要将拿回来的内容返回至调用的位置
return module.exports
}
// 3. 定义 m 属性用于保存 modules
__webpack_require__.m = modules
// 4. 定义 c 属性用于保存cache
__webpack_require__.c = installedModules
// 5. 定义 o 方法用于判断对象的身上是否存在指定的属性
__webpack_require__.o = function (object, property) {
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty(object, property)
}
// 6. 定义 d 方法用于在对象的身上添加指定的属性,同时给该属性提供gatter
__webpack_require__.d = function (exports, name, getter) {
// 对象身上没有该属性
if (!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {enumerable: true, get: getter})
}
}
// 7. 定义 r 方法用于标识当前模块是 es6(esModule) 类型
__webpack_require__.r = function (exports) {
if (typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, {value: "Module"})
}
Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', {value: true})
}
// 8. 定义 n 方法用于设置具体的getter
__webpack_require__.n = function (module) {
let getter = module && module.__esModule ?
function getDefault() {
return module['default']
} :
function getModuleExports() {
return module
}
// 给getter定义a属性,获取方法是getter
__webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter)
return getter
}
// 17 定义 jsonpScriptSrc 来实现 src 的处理
function jsonpScriptSrc(chunkId) {
return __webpack_require__.p + "" + chunkId + ".built.js"
}
// 16 定义 e 方法用于实现: 实现jsonp来加载内容, 利用promise 实现异步加载操作
__webpack_require__.e = function (chunkId) {
// 1 定义一个数组用于存放 promise
let promises = []
// 2 获取 chunkId 对应的 chunk 是否已经完成了加载
let installedChunkData = inStalledChunks[chunkId]
// 3 依据当前是否已完成加载的状态来执行后续的逻辑
if (installedChunkData !== 0) {
if (installedChunkData) {
promises.push(installedChunkData[2])
} else {
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
installedChunkData = inStalledChunks[chunkId] = [resolve, reject]
})
// installedChunkData [resolve,reject,promise]
promises.push(installedChunkData[2] = promise)
// 创建标签
let script = document.createElement('script')
// 设置src
script.src = jsonpScriptSrc(chunkId)
// 写入 script 标签
document.head.appendChild(script)
}
}
// 执行promise
return Promise.all(promises)
}
// 11. 定义 t 方法,用于加载指定 value 的模块内容,之后对内容进行处理再返回
__webpack_require__.t = function (value, mode) {
// 01 加载 value 对应的模块内容( value 一般就是模块id)
// 加载之后的内容又重新赋值给 value 变量
if (mode & 1) {
value = __webpack_require__(value)
}
if (mode & 8) { // 加载了可以直接返回使用的内容
return value
}
// 到这说明没有return
if ((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) {
return value
}
// 如果8和4都不成立,则需要自定义 ns 来通过 default 属性返回内容
let ns = Object.create(null)
__webpack_require__.r(ns)
Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', {enumerable: true, value: value})
if (mode & 2 && typeof value !== 'string') {
for (var key in value) {
__webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function (key) {
return value[key]
}.bind(null, key))
}
}
return ns
}
// 9. 定义 p 属性,用于保存资源访问路径
__webpack_require__.p = ""
// 11/2. 定义变量存放数组
let jsonArray = window['webpackJsonp'] = window['webpackJsonp'] || []
// 12. 保存原生的push方法
let oldJsonpFunction = jsonArray.push.bind(jsonArray)
// 13. 重写push方法
jsonArray.push = webpackJsonpCallback
// 10. 调用 __webpack_require__ 方法执行模块导入与加载操作
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = '<%- entryModuleId %>')
})
({
<% for(let module of modules) { %>
"<%- module.moduleId %>":
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
<%- module._source %>
}),
<% } %>
});
43.生成打包文件

// Compiler.js
const {
Tapable, AsyncSeriesHook, SyncBailHook, SyncHook, AsyncParallelHook
} = require('tapable')
const NormalModuleFactory = require("./NormalModuleFactory");
const Compilation = require("./Compilation");
const Stats = require("./Stats");
const path = require("path");
const mkdirp = require('mkdirp')
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.context = context
this.hooks = {
// ...
emit: new AsyncSeriesHook(['compilation'])
}
}
emitAssets(compilation, callback) {
// 1. 创建dist 2. 写文件
// 定义一个执行文件生成操作的工具方法
const emitFiles = (err) => {
const assets = compilation.assets
let outputPath = this.options.output.path
for (let file in assets) {
let source = assets[file]
let targetPath = path.posix.join(outputPath, file)
this.outputFileSystem.writeFileSync(targetPath, source, 'utf8')
}
callback(err)
}
// 创建目录后写入
this.hooks.emit.callAsync(compilation, (err) => {
mkdirp.sync(this.options.output.path) // 创建dist
emitFiles()
})
}
run(callback) {
console.log('run 方法执行')
const finalCallback = function (err, stats) {
callback(err, stats)
}
const onCompiled = (err, compilation) => {
console.log('onCompiled')
finalCallback(err, new Stats(compilation))
// 最终在这里将处理好的chunk写入指定文件并输出到dist
this.emitAssets(compilation, (err) => {
let stats = new Stats(compilation)
finalCallback(err, stats)
})
}
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(this, (err) => {
this.hooks.run.callAsync(this, (err) => {
this.compile(onCompiled)
})
})
}
// ...
}
module.exports = Compiler
03.Part 3 · Vue.js 框架源码与进阶
01.模块一 手写 Vue Router、手写响应式实现、虚拟 DOM 和 Diff 算法
02.模块二 Vue.js 源码分析(响应式、虚拟 DOM、模板编译和组件化)
03.模块三 Vuex 数据流管理及Vue.js 服务端渲染(SSR)
04.模块四 搭建自己的SSR、静态站点生成(SSG)及封装 Vue.js 组件库
01.任务一:搭建自己的SSR
01.渲染一个Vue实例

#npm i vue vue-server-renderer
npm i vue@2.6.14 vue-server-renderer@2.6.14
const Vue = require('vue')
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer()
const app = new Vue({
template: `
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
</div>
`,
data: {
message: 'malred'
}
})
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
renderer.renderToString(app, (err, html) => {
if (err) throw err
console.log(html)
})

02.结合到Web服务中
npm i express
const Vue = require('vue')
const express = require('express')
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer()
const server = express()
server.get("/", (req, res) => {
const app = new Vue({
template: `
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
</div>
`,
data: {
message: '我是malred'
}
})
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
renderer.renderToString(app, (err, html) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).end('Internal Server Error.')
return
}
// html发送到客户端
// 防止中文乱码
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf8')
// res.end(html)
res.end(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!--编码-->
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
${html}
</body>
</html>
`)
})
})
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
nodemon server.js
03.使用HTML模板
const Vue = require('vue')
const express = require('express')
const fs = require('fs')
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer({
// 解析结果会填入模板里
template: fs.readFileSync("./index.template.html", 'utf-8')
})
const server = express()
server.get("/", (req, res) => {
// ...
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
renderer.renderToString(app, (err, html) => {
// ...
res.end(html)
})
})
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
<!--index.template.html-->
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--内容将渲染到这-->
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->
</body>
</html>
04.在模板中使用外部数据
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<!--3个大括号,直接原文输出,vue不会进行处理-->
{{{ meta }}}
<title>{{ title }}</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--内容将渲染到这-->
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->
</body>
</html>
// ...
server.get("/", (req, res) => {
// ...
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
renderer.renderToString(app, {
// 上下文对象,可以传入数据,在模板里使用
title: '示例页面',
meta: `
<meta name="description" content="一个测试页面"/>
`
}, (err, html) => {
// ...
}
)
})
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
构建配置
05.构建配置-基本思路
需要有客户端脚本,接管服务端渲染好的内容,实现为动态页面


// ...
server.get("/", (req, res) => {
const app = new Vue({
template: `
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
<h2>客户端动态交互</h2>
<div>
<input v-model="message">
</div>
<div>
<button @click="onClick">点击测试</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
data: {
message: '我是malred'
},
methods: {
onClick() {
console.log('Hello World!')
}
}
})
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
renderer.renderToString(
// ...
)
})
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
06.构建配置-源码结构





<script>
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
message: '我是malred'
}
},
methods: {
onClick() {
console.log('Hello World!')
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{message}}</h1>
<h2>客户端动态交互</h2>
<div>
<input v-model="message">
</div>
<div>
<button
@click="onClick">点击测试
</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
// app.js
/**
* 通用启动入口
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 导出一个工厂函数,用于创建新的
// 应用程序 router 和 store 实例
export function createApp() {
const app = new Vue({
// 根实例简单的渲染应用程序组件
render: h => h(App)
})
return {app}
}
// entry-client.js
/**
* 客户端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
// 客户端特定引导逻辑……
const {app} = createApp()
// 这里假定 App.vue 模板中根元素具有 `id="app"`
app.$mount('#app')
// entry-server.js
/**
* 服务端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
export default context => {
const {app} = createApp()
// 服务端路由处理 / 数据预取 ...
return app
}
07.构建配置-安装依赖


npm i cross-env
npm i -D webpack webpack-cli webpack-merge webpack-node-externals @babel/core @babel/plugin-transform-runtime @babel/preset-env babel-loader css-loader url-loader file-loader rimraf vue-loader vue-template-compiler friendly-errors-webpack-plugin
npm i vue-loader@15.10.2
08.构建配置-webpack配置文件


// webpack.base.config.js
/**
* 公共配置
*/
const VueLoaderPlugin = require('vue-loader/lib/plugin')
const path = require('path')
// 友好的日志打印
const FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
// 安全的文件路径
const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)
const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
module.exports = {
mode: isProd ? 'production' : 'development',
output: {
path: resolve('../dist/'),
publicPath: '/dist/',
filename: '[name].[chunkhash].js'
},
resolve: {
alias: {
// 路径别名,@ 指向 src
'@': resolve('../src/')
},
// 可以省略的扩展名
// 当省略扩展名的时候,按照从前往后的顺序依次解析
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json']
},
// 调试信息
devtool: isProd ? 'source-map' : 'cheap-module-eval-source-map',
module: {
rules: [
// 处理图片资源
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif)$/i,
use: [
{
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 8192,
},
},
],
},
// 处理字体资源
{
test: /\.(woff|woff2|eot|ttf|otf)$/,
use: [
'file-loader',
],
},
// 处理 .vue 资源
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader'
},// 处理 CSS 资源
// 它会应用到普通的 `.css` 文件
// 以及 `.vue` 文件中的 `<style>` 块
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'vue-style-loader',
'css-loader'
]
},
// CSS 预处理器,参考:https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/zh/guide/pre-processors.html
// 例如处理 Less 资源
// {
// test: /\.less$/,
// use: [
// 'vue-style-loader',
// 'css-loader',
// 'less-loader'
// ]
// },
]
},
plugins: [
new VueLoaderPlugin(),
new FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin()
]
}
// webpack.client.config.js
/**
* 客户端打包配置
*/
// merge用于合并webpack配置信息
const {merge} = require('webpack-merge')
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base.config.js')
const VueSSRClientPlugin = require('vue-server-renderer/client-plugin')
// 合并baseConfig和当前config
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, {
entry: {
// 该相对路径是相对于执行打包的目录
app: './src/entry-client.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
// ES6 转 ES5
{
test: /\.m?js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-env'],
cacheDirectory: true, plugins: ['@babel/plugin-transform-runtime']
}
}
},
]
},
// 重要信息:这将 webpack 运行时分离到一个引导 chunk 中,
// 以便可以在之后正确注入异步 chunk。
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
name: "manifest",
minChunks: Infinity
}
},
plugins: [
// 此插件在输出目录中生成 `vue-ssr-client-manifest.json`。
new VueSSRClientPlugin()
]
})
// webpack.server.config.js
/**
* 服务端打包配置
*/
const {merge} = require('webpack-merge')
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals')
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base.config.js')
const VueSSRServerPlugin = require('vue-server-renderer/server-plugin')
// 合并配置
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, {
// 将 entry 指向应用程序的 server entry 文件
entry: './src/entry-server.js',
// 这允许 webpack 以 Node 适用方式处理模块加载
// 并且还会在编译 Vue 组件时,
// 告知 `vue-loader` 输送面向服务器代码(server-oriented code)。
target: 'node',
output: {
filename: 'server-bundle.js',
// 此处告知 server bundle 使用 Node 风格导出模块(Node-style exports)
libraryTarget: 'commonjs2'
},
// 不打包 node_modules 第三方包,而是保留 require 方式直接加载
externals: [nodeExternals({
// 白名单中的资源依然正常打包
allowlist: [/\.css$/]
})],
plugins: [
// 这是将服务器的整个输出构建为单个 JSON 文件的插件。
// 默认文件名为 `vue-ssr-server-bundle.json`
new VueSSRServerPlugin()
]
})
09.构建配置-配置构建命令
package.json
{
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"start": "node server.js",
"build:client": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack --config build/webpack.client.config.js",
"build:server": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack --config build/webpack.server.config.js",
"build": "rimraf dist && npm run build:client && npm run build:server"
},
"dependencies": {
"axios": "^0.19.2",
"chokidar": "^3.4.0",
"cross-env": "^7.0.2",
"express": "^4.17.1",
"vue": "^2.6.11",
"vue-meta": "^2.4.0",
"vue-router": "^3.3.4",
"vue-server-renderer": "^2.6.11",
"vuex": "^3.5.1"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "^7.10.4",
"@babel/plugin-transform-runtime": "^7.10.4",
"@babel/preset-env": "^7.10.4",
"babel-loader": "^8.1.0",
"css-loader": "^3.6.0",
"file-loader": "^6.0.0",
"friendly-errors-webpack-plugin": "^1.7.0",
"rimraf": "^3.0.2",
"url-loader": "^4.1.0",
"vue-loader": "^15.9.3",
"vue-template-compiler": "^2.6.11",
"webpack": "^4.43.0",
"webpack-cli": "^3.3.12",
"webpack-dev-middleware": "^3.7.2",
"webpack-hot-middleware": "^2.25.0",
"webpack-merge": "^5.0.9",
"webpack-node-externals": "^2.5.0"
}
}

10.构建配置-启动应用
// server.js
const express = require('express')
const fs = require('fs')
const serverBundle = require('./dist/vue-ssr-server-bundle.json')
const clientManifest = require('./dist/vue-ssr-client-manifest.json')
const template = fs.readFileSync("./index.template.html", 'utf-8')
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createBundleRenderer(
serverBundle, {
// 解析结果会填入模板里
template, clientManifest
})
const server = express()
// 客户端会从server端调用编译后的js,这里需要开放dist目录给客户端
server.use('/dist', express.static('./dist'))
server.get("/", (req, res) => {
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
// 会从entry-server里拿到vue实例
renderer.renderToString({
// ...
}, (err, html) => {
// ...
}
)
})
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
11.构建配置-解析渲染流程
serverBundle文件files就是打包后的js,entry表示入口,map是用于调试的信息,通过entry找到打包后的server-bundle.js,然后得到vue实例


client-manifest描述了客户端构建需要的资源信息,initial中指定的资源会被自动配置到html中,
async中是异步的资源,modules存放的是针对原始模块的依赖信息







构建配置开发模式
12.构建配置开发模式-基本思路
希望写完代码(src下的源代码)能自动重启服务器,自动加载资源文件,自动打开浏览器
{
"scripts": {
"start": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production && node server.js",
"dev": "node server.js"
}
}
// const Vue = require('vue')
const express = require('express')
const fs = require('fs')
const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
// ssr渲染器
let renderer
if (isProd) {
// 生产模式: 基于构建好的文件启动
const serverBundle = require('./dist/vue-ssr-server-bundle.json')
const clientManifest = require('./dist/vue-ssr-client-manifest.json')
const template = fs.readFileSync("./index.template.html", 'utf-8')
renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createBundleRenderer(
serverBundle, {
// 解析结果会填入模板里
template, clientManifest
})
} else {
// 开发模式: 监视打包构建 -> 重新生成renderer
}
const server = express()
// 客户端会从server端调用编译后的js,这里需要开放dist目录给客户端
server.use('/dist', express.static('./dist'))
// 路由处理的渲染函数
const render = (req, res) => {
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
// 会从entry-server里拿到vue实例
renderer.renderToString({
// 上下文对象,可以传入数据,在模板里使用
title: '示例页面',
meta: `
<meta name="description" content="一个测试页面"/>
`
}, (err, html) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).end('Internal Server Error.')
return
}
// html发送到客户端
// 防止中文乱码
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf8')
// res.end(html)
res.end(html)
}
)
}
server.get("/", isProd ?
render
: (req, res) => {
// TODO: 等待renderer重新构建完成后,再调用render渲染
render()
}
)
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
13.构建配置开发模式-提取处理模块
// build/setup-dev-server.js
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
const onReady = new Promise()
// 监视构建 -> 更新renderer
return onReady
}
// const Vue = require('vue')
const express = require('express')
const fs = require('fs')
const {createBundleRenderer} = require('vue-server-renderer')
const setupDevServer = require('./build/setup-dev-server')
const server = express()
const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
// ssr渲染器
let renderer
// 开发模式是否构建renderer完成
let onReady
if (isProd) {
// 生产模式: 基于构建好的文件启动
const serverBundle = require('./dist/vue-ssr-server-bundle.json')
const clientManifest = require('./dist/vue-ssr-client-manifest.json')
const template = fs.readFileSync("./index.template.html", 'utf-8')
renderer = createBundleRenderer(
serverBundle, {
// 解析结果会填入模板里
template, clientManifest
})
} else {
// 开发模式: 监视打包构建 -> 重新生成renderer
onReady = setupDevServer(server, (serverBundle, template, clientManifest) => {
renderer = createBundleRenderer(
serverBundle, {
// 解析结果会填入模板里
template, clientManifest
})
})
}
// 客户端会从server端调用编译后的js,这里需要开放dist目录给客户端
server.use('/dist', express.static('./dist'))
// 路由处理的渲染函数
const render = (req, res) => {
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
// 会从entry-server里拿到vue实例
renderer.renderToString({
// ...
}, (err, html) => {
// ...
}
)
}
server.get("/", isProd ?
render
: async (req, res) => {
// 等待renderer重新构建完成后,再调用render渲染
await onReady
render()
}
)
server.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('server running at port 3001.')
})
14.构建配置开发模式-update更新函数
// setup-dev-server.js
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
let ready // promise的结果
const onReady = new Promise(r => ready = r)
// 监视构建 -> 更新renderer
let template
let serverBundle
let clientManifest
const update = () => {
if (serverBundle && template && clientManifest) {
ready()
callback(serverBundle, template, clientManifest)
}
}
// 监视构建template -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
// 监视构建serverBundle -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
// 监视构建clientManifest -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
return onReady
}
15.构建配置开发模式-处理模板文件
// setup-dev-server.js
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const chokidar = require("chokidar")
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
let ready // promise的结果
const onReady = new Promise(r => ready = r)
// 监视构建 -> 更新renderer
let template
let serverBundle
let clientManifest
const update = () => {
if (serverBundle && template && clientManifest) {
ready()
callback(serverBundle, template, clientManifest)
}
}
// 监视构建template -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
const tempPath = path.resolve(__dirname, '../index.template.html')
template = fs.readFileSync(tempPath, 'utf-8')
update()
// console.log(template)
// 监视: fs.watch | fs.watchFile
// 使用第三方库, 监视文件改变
chokidar.watch(tempPath).on('change', () => {
// console.log('template change')
template = fs.readFileSync(tempPath, 'utf-8')
update()
})
// 监视构建serverBundle -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
// 监视构建clientManifest -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
return onReady
}
16.构建配置开发模式-服务端监视打包
// setup-dev-server.js
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const chokidar = require("chokidar")
const webpack = require('webpack')
const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
// ...
// 监视构建serverBundle -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
const serverConfig = require('./webpack.server.config')
// 通过webpack创建编译器
const serverCompiler = webpack(serverConfig)
// 执行打包构建,并监视变化
serverCompiler.watch({}, (err, stats) => {
if (err) throw err
if (stats.hasErrors()) return
// console.log('success')
// 不用require是因为require有缓存,文件再次加载会用缓存
serverBundle = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync(
resolve("../dist/vue-ssr-server-bundle.json"), 'utf-8')
)
// console.log(serverBundle)
update()
})
// 监视构建clientManifest -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
return onReady
}
17.构建配置开发模式-把数据写入内存中


npm i webpack-dev-middleware --save-dev
// setup-dev-server.js
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const chokidar = require("chokidar")
const webpack = require('webpack')
const devMiddleware = require('webpack-dev-middleware')
const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
// ...
// 监视构建serverBundle -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
const serverConfig = require('./webpack.server.config')
// 通过webpack创建编译器
const serverCompiler = webpack(serverConfig)
// 缓存在内存,自动监听并打包
const serverDevMiddleware = devMiddleware(serverCompiler, {
// 关闭日志输出,由FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin处理
logLevel: 'silent'
});
// 编译器的钩子,相对于注册了插件
serverCompiler.hooks.done.tap('server', () => {
serverBundle = JSON.parse(
// devMiddleware的文件读写方法
serverDevMiddleware.fileSystem.readFileSync(
resolve("../dist/vue-ssr-server-bundle.json"), 'utf-8')
)
// console.log(serverBundle)
update()
})
// 监视构建clientManifest -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
return onReady
}
18.构建配置开发模式-客户端构建
// setup-dev-server.js
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const chokidar = require("chokidar")
const webpack = require('webpack')
const devMiddleware = require('webpack-dev-middleware')
const serverConfig = require("./webpack.server.config");
const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
// ...
// 监视构建clientManifest -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
const clientConfig = require('./webpack.client.config')
// 通过webpack创建编译器
const clientCompiler = webpack(clientConfig)
// 缓存在内存,自动监听并打包
const clientDevMiddleware = devMiddleware(clientCompiler, {
// 请求资源url的前缀
publicPath: clientConfig.output.publicPath,
// 关闭日志输出,由FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin处理
logLevel: 'silent'
});
// 编译器的钩子,相对于注册了插件
clientCompiler.hooks.done.tap('client', () => {
clientManifest = JSON.parse(
// devMiddleware的文件读写方法
clientDevMiddleware.fileSystem.readFileSync(
resolve("../dist/vue-ssr-client-manifest.json"), 'utf-8')
)
// console.log(clientManifest)
update()
})
// !!!将clientDevMiddleware挂载到express服务中,提供对其内存中文件的访问
server.use(clientDevMiddleware)
return onReady
}
// server.js
// 客户端会从server端调用编译后的js,这里需要开放dist目录给客户端
// 处理的是物理磁盘的文件,而我们现在是内存里的文件
server.use('/dist', express.static('./dist'))
server.get("/", isProd ?
render
: async (req, res) => {
// 等待renderer重新构建完成后,再调用render渲染
await onReady
render(req, res)
}
)
19.构建配置开发模式-热更新
npm i --save-dev webpack-hot-middleware






// setup-dev-server.js
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const chokidar = require("chokidar")
const webpack = require('webpack')
const devMiddleware = require('webpack-dev-middleware')
const hotMiddleware = require('webpack-hot-middleware')
const serverConfig = require("./webpack.server.config");
const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)
module.exports = (server, callback) => {
// ...
// 监视构建clientManifest -> 调用update -> 更新renderer渲染器
const clientConfig = require('./webpack.client.config')
// 热更新插件
clientConfig.plugins.push(new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin())
clientConfig.entry.app = [
'webpack-hot-middleware/client?quiet=true&reload=true',// 和服务端交互处理热更新的一个客户端脚本
clientConfig.entry.app// 原本的入口
]
// 热更新需要每次打包的文件名(hash)一致
clientConfig.output.filename = '[name].js'
// 通过webpack创建编译器
const clientCompiler = webpack(clientConfig)
// ...
// 热更新服务
server.use(hotMiddleware(clientCompiler, {
log: false // 关闭本身的日志
}))
// !!!将clientDevMiddleware挂载到express服务中,提供对其内存中文件的访问
server.use(clientDevMiddleware)
return onReady
}
20.编写通用应用注意事项






路由处理
21.路由处理-配置VueRouter


npm i vue-router
// router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import Home from '@/pages/Home'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
export const createRouter = () => {
const router = new VueRouter({
// 兼容前后端(服务端/客户端)
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: "/",
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
{
path: "/about",
name: 'about',
// 异步加载组件
component: () => import("@/pages/About")
},
{
path: "*",
name: 'error404',
// 异步加载组件
component: () => import("@/pages/404")
},
]
})
return router
}
22.路由处理-将路由注册到根实例
// src/app.js
/**
* 通用启动入口
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import {createRouter} from "./router";
// 导出一个工厂函数,用于创建新的
// 应用程序 router 和 store 实例
export function createApp() {
const router = createRouter()
// 每次创建的都是独立的vue实例
const app = new Vue({
router, // 路由挂载到根实例
// 根实例简单的渲染应用程序组件
render: h => h(App),
})
return {app, router}
}
23.路由处理-适配服务端入口

// entry-server.js
/**
* 服务端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
// export default context => {
// // 因为有可能会是异步路由钩子函数或组件,所以我们将返回一个 Promise,
// // 以便服务器能够等待所有的内容在渲染前,
// // 就已经准备就绪。
// return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// const {app, router} = createApp()
//
// // 设置服务器端 router 的位置
// router.push(context.url)
//
// // 等到 router 将可能的异步组件和钩子函数解析完
// router.onReady(() => {
// const matchedComponents = router.getMatchedComponents()
// // 匹配不到的路由,执行 reject 函数,并返回 404
// if (!matchedComponents.length) {
// return reject({code: 404})
// }
//
// // Promise 应该 resolve 应用程序实例,以便它可以渲染
// resolve(app)
// }, reject)
// })
// }
export default async context => {
// async返回的就是promise
const {app, router} = createApp()
// 设置服务器端 router 的位置
router.push(context.url)
// 等到 router 将可能的异步组件和钩子函数解析完
// new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
// router.onReady(resolve,reject)
// })
await new Promise(router.onReady.bind(router))
// async 会把非promise数据包装到promise
return app
}
24.路由处理-服务端server适配
// server.js
// ...
// 路由处理的渲染函数
const render = async (req, res) => {
try {
// 渲染为纯文本字符串
// 会从entry-server里拿到vue实例
const html = await renderer.renderToString({
// 上下文对象(context),可以传入数据,在模板里使用
title: '示例页面',
meta: `
<meta name="description" content="一个测试页面"/>
`,
url: req.url
})
// html发送到客户端
// 防止中文乱码
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf8')
// res.end(html)
res.end(html)
} catch (e) {
res.status(500).end('Internal Server Error.')
}
}
// 服务端路由设置*,意味着所有url路由都会进入这里
// 进入渲染路由处理,然后渲染完传递给entry-server
server.get("*", isProd ?
render
: async (req, res) => {
// 等待renderer重新构建完成后,再调用render渲染
await onReady
render(req, res)
}
)
25.路由处理-适配客户端入口

// entry-client.js
/**
* 客户端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
// 客户端特定引导逻辑……
const {app, router} = createApp()
// 这里假定 App.vue 模板中根元素具有 `id="app"`
// app.$mount('#app')
router.onReady(() => {
app.$mount('#app')
})
26.路由处理-处理完成
下载js,并不运行,防止阻塞;
preload加载一定会用到的资源
prefetch是浏览器空闲时加载的接下来可能用到的资源

// app.vue
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link>
</li>
<li>
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
<!-- 路由出口 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
27.管理页面Head内容


npm i vue-meta
// src/app.js
/**
* 通用启动入口
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import {createRouter} from "./router";
import VueMeta from "vue-meta";
Vue.use(VueMeta)
Vue.mixin({
metaInfo: {
// 页面的标题渲染到%s
titleTemplate: '%s - malred'
}
})
// ...
// entry-server.js
/**
* 服务端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
export default async context => {
// async返回的就是promise
const {app, router} = createApp()
// 在路由导航之前得到并设置meta
const meta = app.$meta()
// 设置服务器端 router 的位置
router.push(context.url)
// 合并页面meta和通用meta
context.meta = meta
// 等到 router 将可能的异步组件和钩子函数解析完
// new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
// router.onReady(resolve,reject)
// })
await new Promise(router.onReady.bind(router))
// async 会把非promise数据包装到promise
return app
}
<!--index.template.html-->
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
{{{ meta.inject().title.text() }}}
{{{ meta.inject().meta.text() }}}
</head>
<body>
<!--内容将渲染到这-->
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->
</body>
</html>
// Home.vue
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
metaInfo:{
title:'首页'
}
}
</script>
数据预取和状态管理
28.数据预取和状态管理-思路分析
通过服务端渲染,将从数据接口得到的数据渲染到页面,这里面有一些挑战



// post.vue
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: "Posts",
data() {
return {
posts: []
}
},
// 服务端渲染只能用beforeCreate和created
// 服务端渲染不会等待异步操作
// 所以在服务端渲染axios获取数据不会生效
async created() {
console.log('Posts Created Start')
const {data} = await axios({
method: 'GET',
url: 'http://localhost:8848/topics'
})
// this.posts = data.data
this.posts = data
console.log('Posts Created End')
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>Post List</h1>
<ul>
<!-- 虽然服务端不能得到数据,但是客户端会请求获取数据并渲染 -->
<li v-for="post in posts"
:key="post.id">{{post.title}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
29.数据预取和状态管理-数据预取
// src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import axios from "axios";
Vue.use(Vuex)
export const createStore = () => {
return new Vuex.Store({
// 单独的函数返回,防止交叉请求可能带来的污染
state: () => ({
posts: []
}),
// 修改数据状态的
mutations: {
setPosts(state, data) {
console.log(data)
state.posts = data
}
},
// 可以执行异步操作
// 服务端渲染期间最好让action返回一个promise
// 因为服务端渲染会等待每个promise完成后再渲染字符串
actions: {
// async 默认返回promise
async getPosts({commit}) {
const {data} = await axios.get('http://localhost:8848/topics')
// 调用mutations里定义的函数
console.log(data)
// commit('setPosts', data.data)
commit('setPosts', data)
}
}
})
}
// src/app.js
/**
* 通用启动入口
*/
import {createStore} from "./store";
// ...
// 导出一个工厂函数,用于创建新的
// 应用程序 router 和 store 实例
export function createApp() {
const router = createRouter()
const store = createStore()
// 每次创建的都是独立的vue实例
const app = new Vue({
router, // 路由挂载到根实例
store, // 容器挂载到根实例
// 根实例简单的渲染应用程序组件
render: h => h(App),
})
return {app, router, store}
}
// Posts.vue
<script>
import {mapState, mapActions} from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Posts",
computed: {
...mapState(['posts'])
},
// Vue SSR 特别为服务端渲染提供的生命周期hook函数
serverPrefetch() {
// 发起action, 返回promise
// this.$store.dispatch('getPosts')
return this.getPosts();
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['getPosts'])
}
}
</script>
运行时发现, 有一瞬间渲染出来title, 但是又没了, 因为服务端和客户端数据不一致, 水合失败, 客户端重新渲染, 导致丢失数据
30.数据预取和状态管理-将预取数据同步到客户端



// entry-server.js
/**
* 服务端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
export default async context => {
// async返回的就是promise
const {app, router, store} = createApp()
// 在路由导航之前得到并设置meta
const meta = app.$meta()
// 设置服务器端 router 的位置
router.push(context.url)
// 合并页面meta和通用meta
context.meta = meta
// 等到 router 将可能的异步组件和钩子函数解析完
// new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
// router.onReady(resolve,reject)
// })
await new Promise(router.onReady.bind(router))
// 服务端渲染数据完毕后被调用,可以拿到服务端渲染好的容器数据
context.rendered = () => {
// 合并到将给客户端的state
context.state = store.state
}
// async 会把非promise数据包装到promise
return app
}
// entry-client.js
/**
* 客户端启动入口
*/
import {createApp} from './app'
// 客户端特定引导逻辑……
const {app, router, store} = createApp()
// 这里假定 App.vue 模板中根元素具有 `id="app"`
// app.$mount('#app')
if (window.__INITIAL_STATE__) {
// 将服务端给的store给到客户端
store.replaceState(window.__INITIAL_STATE__)
}
router.onReady(() => {
app.$mount('#app')
})
05.模块五 Vue.js 3.0 Composition APIs 及 3.0 原理剖析
04.任务四:Vite 实现原理
01.Vite











02.Vite 实现原理-静态Web服务器






// index.js
#!/usr/
bin / env
node
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const app = new Koa()
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
await send(ctx, ctx.path, {root: process.cwd(), index: 'index.html'})
await next()
})
app.listen(5173)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:5173')
03.Vite 实现原理-修改第三方模块的路径


// index.js
#!/usr/
bin / env
node
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const app = new Koa()
// 将文件流转字符串
const streamToStr = stream => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const chunks = []
// 不同事件的处理
stream.on('data', chunk => chunks.push(chunk))
stream.on('end', () => resolve(Buffer.concat(chunks).toString('utf-8')))
stream.on('error', reject)
})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
await send(ctx, ctx.path, {root: process.cwd(), index: 'index.html'})
await next()
})
// 返回静态文件时,先判断是不是第三方模块,如果是,就返回模块路径
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.type === 'application/javascript') {
const contents = await streamToStr(ctx.body)
// import vue from 'vue' 第三方模块需要改为@module/xxx
// import app from './app.vue' 相对路径不需要处理,可以正常引入
ctx.body = contents.replace(/(from\s+['"])(?!\.\/)/g, '$1/@modules/')
}
})
app.listen(5173)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:5173')
04.Vite 实现原理-加载第三方模块



// index.js
#!/usr/
bin / env
node
const path = require('path')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const app = new Koa()
// 将文件流转字符串
const streamToStr = stream => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// ...
})
// 3. 加载第三方模块
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// ctx.path --> /@modules/vue
if (ctx.path.startsWith('/@modules/')) {
const moduleName = ctx.path.substr(10)
const pkgPath = path.join(process.cwd(), 'node_modules', moduleName, 'package.json')
const pkg = require(pkgPath)
// pkg.module -> 入口文件
ctx.path = path.join('/node_modules', moduleName, pkg.module)
}
await next()
})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
// 返回静态文件时,先判断是不是第三方模块,如果是,就返回模块路径
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
app.listen(5173)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:5173')
05.Vite 实现原理-编译单文件组件



#!/usr/bin/env node
const path = require('path')
const {Readable} = require('stream')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const compilerSFC = require('@vue/compiler-sfc')
const app = new Koa()
// 将文件流转字符串
const streamToStr = stream => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// ...
})
const stringToSteam = text => {
const stream = new Readable()
stream.push(text)
stream.push(null)
return stream
}
// 3. 加载第三方模块
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
// 4. 处理单文件组件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.path.endsWith('.vue')) {
const contents = await streamToStr(ctx.body)
// 可以通过descriptor获取编译后的js代码
const {descriptor} = compilerSFC.parse(contents);
let code
// 第一次请求
if (!ctx.query.type) {
// vue2是script,vue3是scriptSetup
if (descriptor.script) {
code = descriptor.script.content
code = code.replace(/export\s+default\s+/g, 'const __script = ')
}
// 不是很懂怎么搞setup
// else {
// code = descriptor.scriptSetup.content
// code = code.replace(/import\s*(\w+)\s*from\s*['"]([^'"\/.]*)['"]/g, `
// const __script =
// `)
// }
code += `
import { render as __render } from '${ctx.path}?type=template'
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`
}
ctx.type = 'application/javascript'
ctx.body = stringToSteam(code)
}
await next()
})
// 返回静态文件时,先判断是不是第三方模块,如果是,就返回模块路径
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.type === 'application/javascript') {
const contents = await streamToStr(ctx.body)
// import vue from 'vue' 第三方模块需要改为@module/xxx
// import app from './app.vue' 相对路径不需要处理,可以正常引入
ctx.body = contents.replace(/(from\s+['"])(?![\.\/])/g, '$1/@modules/')
}
await next()
})
app.listen(5173)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:5173')
06.Vite 实现原理-编译单文件组件

#!/usr/bin/env node
const path = require('path')
const {Readable} = require('stream')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const compilerSFC = require('@vue/compiler-sfc')
const app = new Koa()
// 将文件流转字符串
const streamToStr = stream => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const chunks = []
// 不同事件的处理
stream.on('data', chunk => chunks.push(chunk))
stream.on('end', () => resolve(Buffer.concat(chunks).toString('utf-8')))
stream.on('error', reject)
})
const stringToSteam = text => {
const stream = new Readable()
stream.push(text)
stream.push(null)
return stream
}
// 3. 加载第三方模块
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// ctx.path --> /@modules/vue
if (ctx.path.startsWith('/@modules/')) {
const moduleName = ctx.path.substr(10)
const pkgPath = path.join(process.cwd(), 'node_modules', moduleName, 'package.json')
const pkg = require(pkgPath)
// pkg.module -> 入口文件
ctx.path = path.join('/node_modules', moduleName, pkg.module)
}
await next()
})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
await send(ctx, ctx.path, {root: process.cwd(), index: 'index.html'})
await next()
})
// 4. 处理单文件组件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.path.endsWith('.vue')) {
const contents = await streamToStr(ctx.body)
// 可以通过descriptor获取编译后的js代码
const {descriptor} = compilerSFC.parse(contents);
let code
// 第一次请求
if (!ctx.query.type) {
// vue2是script,vue3是scriptSetup
if (descriptor.script) {
code = descriptor.script.content
code = code.replace(/export\s+default\s+/g, 'const __script = ')
}
// 不是很懂怎么搞setup
// else {
// code = descriptor.scriptSetup.content
// code = code.replace(/import\s*(\w+)\s*from\s*['"]([^'"\/.]*)['"]/g, `
// const __script =
// `)
// }
code += `
import { render as __render } from "${ctx.path}?type=template"
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`
}
// 第二次请求
else if (ctx.query.type === 'template') {
// 编译模板
const templateRender =
compilerSFC.compileTemplate({source: descriptor.template.content})
code = templateRender.code
}
ctx.type = 'application/javascript'
ctx.body = stringToSteam(code)
}
await next()
})
// 返回静态文件时,先判断是不是第三方模块,如果是,就返回模块路径
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.type === 'application/javascript') {
const contents = await streamToStr(ctx.body)
// import vue from 'vue' 第三方模块需要改为@module/xxx
// import app from './app.vue' 相对路径不需要处理,可以正常引入
ctx.body = contents
.replace(/(from\s+['"])(?![\.\/])/g, '$1/@modules/')
// 替换process.env.NODE_ENV
.replace(/process\.env\.NODE_ENV/g, '"development"')
}
await next()
})
app.listen(5173)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:5173')

06.模块六 Vue.js + Vuex + TypeScript 实战项目开发与项目优化
07.模块七 Vue.js 3 + Vite + TypeScript 实战项目开发
01.任务一:搭建项目架构(上)
01.01 项目初始化

npm init vite@latest


02.02 代码规范和ESLint-基础配置
npm i eslint --save-dev
npx eslint --init
{
"scripts": {
"lint": "eslint ./src/**/*.{js,jsx,vue,ts,tsx} --fix"
}
}
// eslint.cjs
module.exports = {
"env": {
"browser": true,
"es2021": true
},
"extends": [
"standard-with-typescript",
"plugin:vue/vue3-essential"
],
"overrides": [
{
"env": {
"node": true
},
"files": [
".eslintrc.{js,cjs}"
],
"parserOptions": {
"sourceType": "script"
}
}
],
"parserOptions": {
"ecmaVersion": "latest",
extraFileExtensions: ['.vue'],
parser: "@typescript-eslint/parser",
project: ["tsconfig.json"],
"sourceType": "module"
},
"plugins": [
"vue"
],
"rules": {}
}
03.03 代码规范和ESLint-编辑器集成
04.04 代码规范和ESLint-配置commit钩子


npx mrm@2 lint-staged
05.05 代码规范和ESLint-在开发和构建的时候进行验证
npm install eslint vite-plugin-eslint --save-dev
import {defineConfig} from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
import eslint from 'vite-plugin-eslint'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue(), eslint({
cache: false // 禁用eslint缓存
})],
})
06.06 GitCommit规范
















npm i --save-dev @commitlint/config-conventional @commitlint/cli
npx husky add .husky/commit-msg 'npx --no-install commitlint --edit "$1"'
07.07 Vite中的TS环境说明


08.08 Vue3中的TS支持


















09.09 Vue3中的script-setup语法

04.Part 4 · React 框架原理与实战
03.模块三 React Hooks、Chakra-UI、组件性能优化、封装组件库
04.模块四 React 服务端渲染专题(原生实现、Next.js 集成框架、Gatsby)
01.任务一:ReactSSR
01.ReactSSR相关观念回顾






02.项目结构初始化
pnpm import package-lock.json
pnpm install

03.实现ReactSSR雏形


// server/http.js
import express from 'express'
const app = express();
const port = 3001
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`app is running in ${port}`)
})
export default app
// server/index.js
import React from "react"; // 不引入会报错 React is not defined
import app from './http.js'
import Home from "../share/pages/Home.js";
import {renderToString} from "react-dom/server";
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
// Home组件包含jsx语法, 要引入jsx
const content = renderToString(<Home/>)
res.send(`
<html>
<head>
<title>react ssr</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
</body>
</html>
`)
})

// share/pages/Home.js
import React from "react"
function Home() {
return <div>Home works</div>
}
export default Home
04.服务器端程序webpack打包配置


// webpack.server.js
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
// 运行在什么环境下
target: 'node',
entry: './src/server/index.js',
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'build'),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"]
}
}
}
]
}
}
webpack --config webpack.server.js
node build/bundle.js


05.为组件元素附加事件的方式



// webpack.client.js
const path = require('path');
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals');
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
// 在浏览器运行, 不需要node环境运行
// target: 'node',
entry: './src/client/index.js',
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
// externals: [nodeExternals()],
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"]
}
}
}
]
}
}
// src/client/index.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import Home from '../share/pages/Home'
// 重新渲染Home组件, 并附加js
// hydrate重新渲染会复用dom组件
ReactDOM.hydrate(<Home/>, document.getElementById('root'))




06.优化:合并webpack配置

// webpack.base.js
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"]
}
}
}
]
}
}
// webpack.client.js
const path = require('path');
const merge = require('webpack-merge'); // 用于合并webpack配置
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base')
const config = {
entry: './src/client/index.js',
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
}
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, config)
// webpack.server.js
const path = require('path');
const merge = require('webpack-merge'); // 用于合并webpack配置
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base')
const config = {
// 运行在什么环境下
target: 'node',
entry: './src/server/index.js',
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'build'),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
}
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, config)
07.优化:合并项目启动命令


08.优化:服务器端打包文件体积优化


// webpack.server.js
const path = require('path');
const merge = require('webpack-merge'); // 用于合并webpack配置
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base')
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals'); // 用于减少服务端打包体积
const config = {
// 运行在什么环境下
target: 'node',
entry: './src/server/index.js',
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'build'),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
// 排除node系统模块
externals: [nodeExternals()]
}
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, config)
09.优化:代码拆分

// src/server/renderer.js
import React from "react"; // 不引入会报错
import Home from "../share/pages/Home.js";
import {renderToString} from "react-dom/server";
// 单独的渲染方法
export default () => {
const content = renderToString(<Home/>)
return `
<html>
<head>
<title>react ssr</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
<!--拿到client打包的js-->
<script src="bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
`
}
// src/server/index.js
import app from './http.js'
import renderer from './renderer'
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(renderer())
})
10.实现服务器端路由




// src/share/pages/List.js
import React from "react";
function List() {
return <div>list page works</div>
}
export default List
// src/server/renderer.js
import React from "react"; // 不引入会报错
import Home from "../share/pages/Home.js";
import {renderToString} from "react-dom/server";
import {StaticRouter} from 'react-router-dom'
import routes from "../share/routes";
import {renderRoutes} from 'react-router-config'
// 单独的渲染方法
export default req => {
const content = renderToString(
<StaticRouter location={req.path}>{renderRoutes(routes)}</StaticRouter>
)
return `
<html>
<head>
<title>react ssr</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
<!--拿到client打包的js-->
<script src="bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
`
}
// src/share/routes.js
import Home from "./pages/Home";
import List from "./pages/List";
export default [
{
path: "/",
component: Home,
exact: true
},
{
path: "/list",
component: List,
}
]



11.实现客户端路由


// src/share/pages/Home.js
import React from "react";
import {Link} from 'react-router-dom'
function Home() {
return <div onClick={() => console.log('Hello V2')}>
Home works
{/*测试客户端路由*/}
<Link to={'/list'}>jump to list</Link>
</div>
}
export default Home
// src/client/index.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import Home from '../share/pages/Home'
import {BrowserRouter} from 'react-router-dom'
import {renderRoutes} from 'react-router-config'
import routes from "../share/routes";
// 重新渲染Home组件, 并附加js
// hydrate重新渲染会复用dom组件
ReactDOM.hydrate(
<BrowserRouter>
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById('root')
)
12.实现客户端Redux

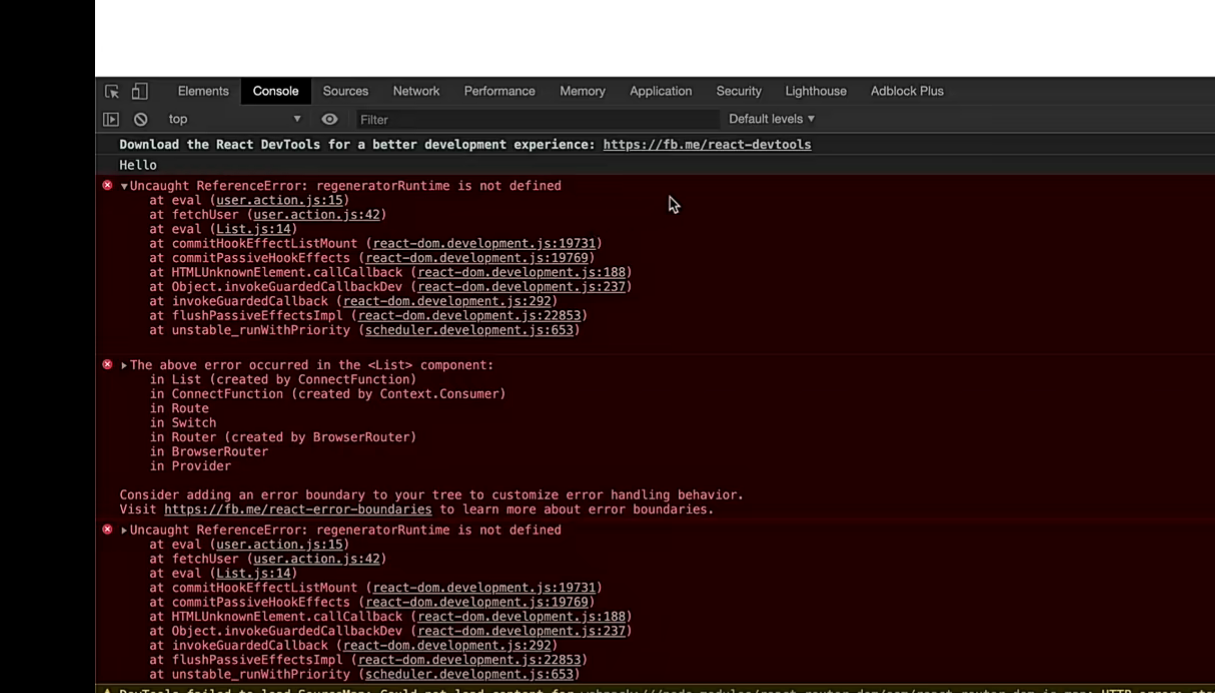
error …
05.模块五 React + Redux + Ant Design + TypeScript 实战
01.任务一:基础配置
01.项目介绍

02.技术栈介绍

03.安装mongodb数据库软件


05.Part 5 · Node.js 全栈开发
01.模块一 Node.js 高级编程(核心模块、模块加载机制)
02.模块二 NoSQL 数据库(MongoDB、Redis)
03.模块三 Web 开发框架(Express 与 Koa)
04.模块四 GraphQL API 开发
01.任务一:GraphQL入门,Scheme和类型

02.使用GraphQL.j
npm init -y
npm install graphql --save
const {graphql, buildSchema} = require('graphql');
// 1. 使用graphql schema语法构建schema
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
foo: String
count: Int
}
`)
// 2. 定义schema的resolver
const rootValue = {
foo() {
return 'bar'
},
count() {
return 123
}
}
// 3. 查询
let source = '{ foo }'
// arg: {schema:xxx, source:xxx, rootValue:xxx}
graphql({schema, source, rootValue}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
source = '{ foo, count }'
// arg: {schema:xxx, source:xxx, rootValue:xxx}
graphql({schema, source, rootValue}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
03.结合Expre服务

npm i express express-graphql graphql --save



const {graphql, buildSchema} = require('graphql');
const express = require('express')
const {graphqlHTTP} = require('express-graphql')
const app = express()
// 1. 使用graphql schema语法构建schema
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
foo: String
count: Int
}
`)
// 2. 定义schema的resolver
const rootValue = {
foo() {
return 'bar'
},
count() {
return 123
}
}
// 3. 挂载graphql中间件
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema,
rootValue,
// 开启浏览器graphql IDE工具
graphiql: true
}))
app.listen(4000, () => {
console.log('server is running at 4000 port')
})
04.客户端
npm i cors
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
axios({
// graphql 请求方法必须是post
method: 'POST',
url: 'http://localhost:4000/graphql',
data: {
query: '{ foo, count }'
}
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
const {graphql, buildSchema} = require('graphql');
const express = require('express')
const {graphqlHTTP} = require('express-graphql')
const cors = require('cors')
const app = express()
// 跨域
app.use(cors())
// ...

05.Query类型



06.标量类型


07.对象类型



// 1. 使用graphql schema语法构建schema
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
foo: String
count: Int
price: Float
flag: Boolean
id: ID
user: User
article: Article
}
type Article {
title: String
body: String
author: User
}
type User {
name: String
age: Int
}
`)
// 2. 定义schema的resolver
const rootValue = {
foo() {
return 'bar'
},
count() {
return 123
},
price() {
return 1.5
},
flag() {
return true
},
id() {
return "fiklsdrhjfgvierhu"
},
user() {
return {
name: 'Jack',
age: 18
}
},
article() {
return {
title: '标题',
body: '内容',
author: {
name: 'Jack',
age: 18
}
}
}
}
08.数组类型
06.Part 6 · 泛客户端开发
07.Part 7 · 商业技术解决方案与高阶技术专题
01.模块一 微前端解决方案
02.模块二 前端自动化测试专题
03.模块三 前端数据可视化专题
04.模块四 前端性能优化专题
01.任务一
01.性能优化介绍













02.Web性能指标介绍









![mksz583-基于Flutter3.x实战跨平台短视频App混合开发[完结]](/medias/featureimages/22.jpg)